Domotz allows you to monitor TCP Services available on your connected devices.
How to monitor TCP Services
In order to monitor TCP services exposed by a device, go to the TCP tab within the Device screen:
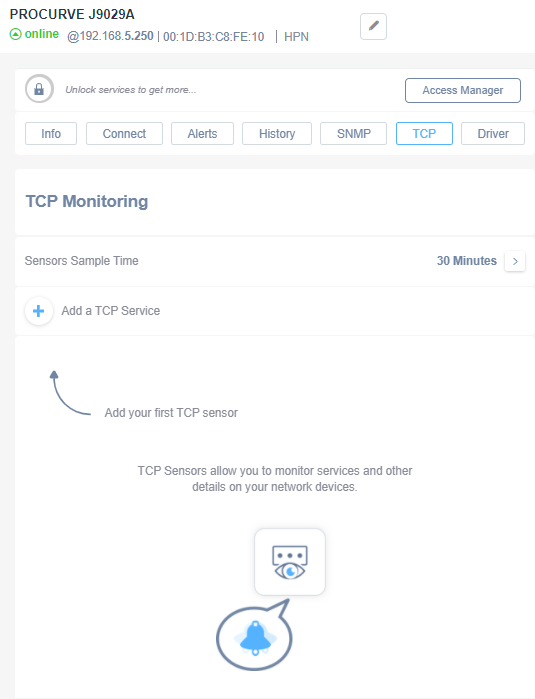
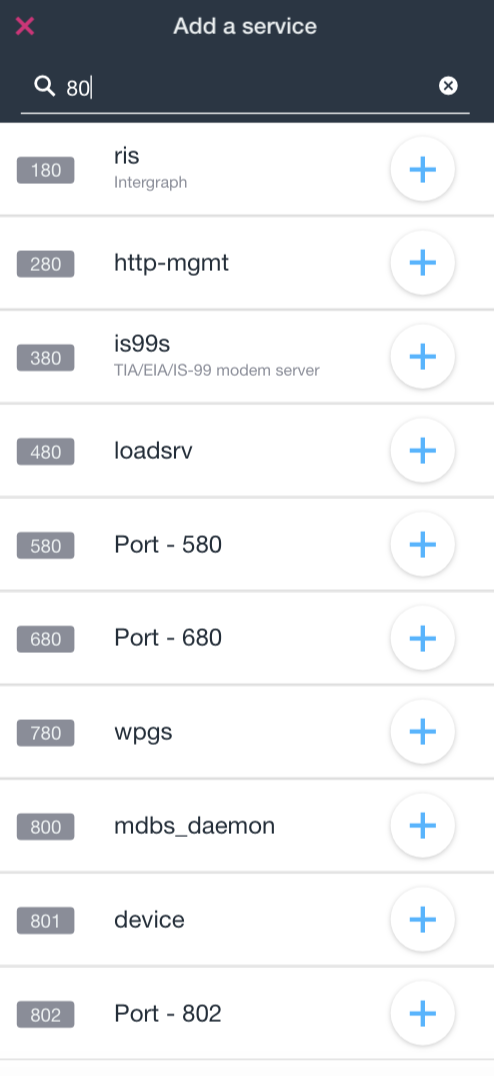
You can add a service to be monitored by clicking on “Add a TCP Service” and entering the name of the service or TCP port number associated.
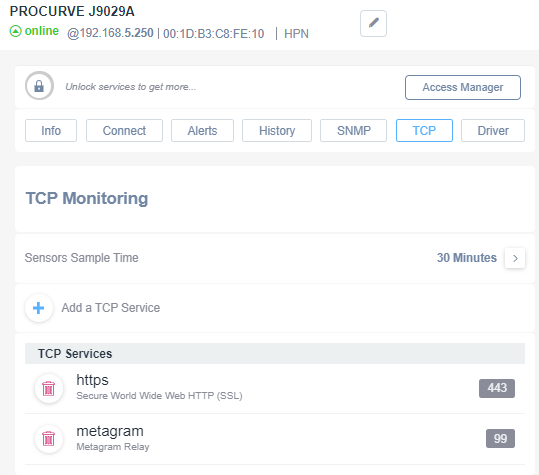
Once the TCP service is added, the Domotz Agent will start monitoring that service. The port will be marked as available (green) if the Service is available on that port or unavailable (red) if not:
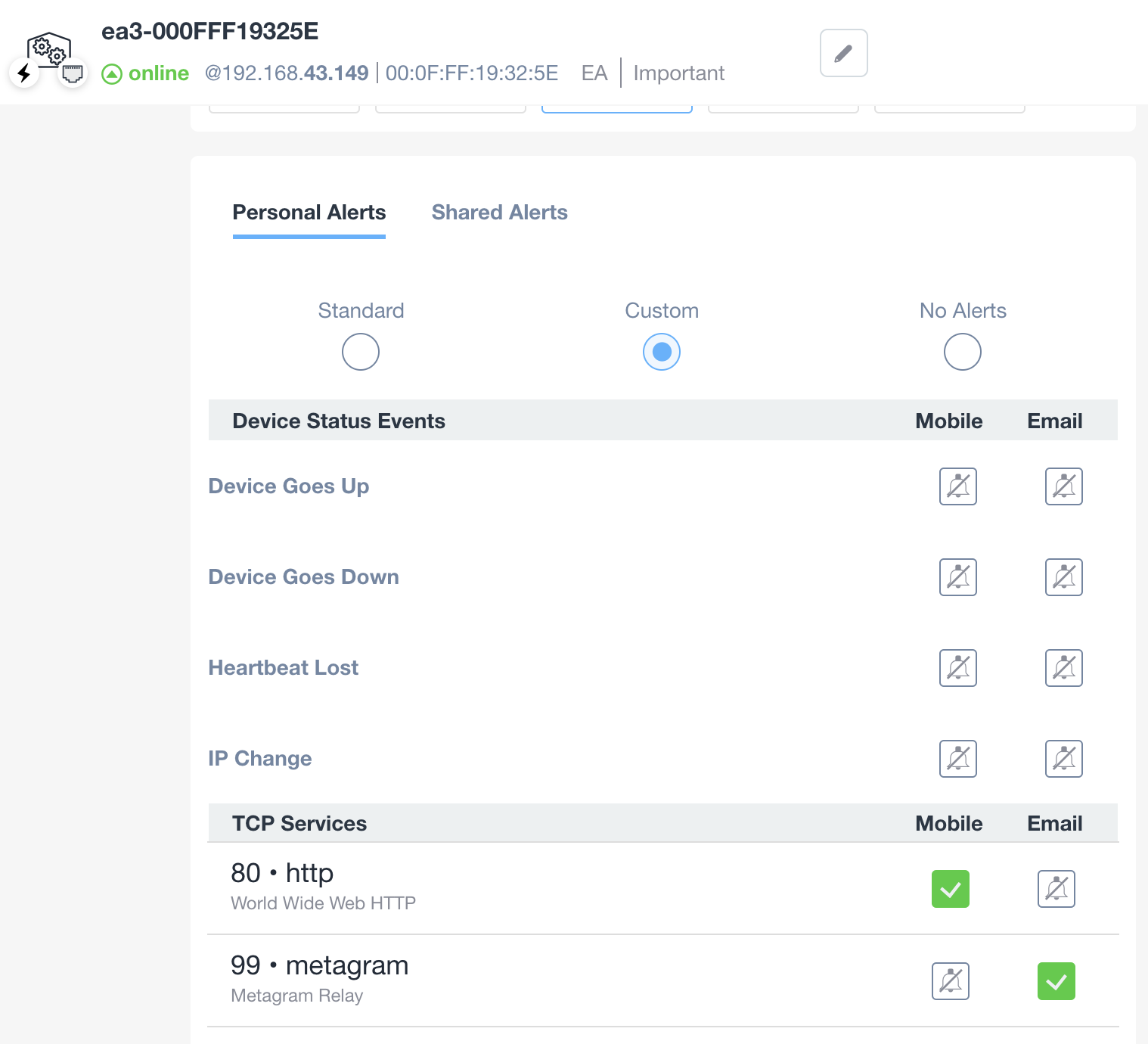
On every single TCP service monitored, the user can set a “Custom” alert (from the Alerts tab) to be informed when the service change status (from available to unavailable and vice-versa):
Learn about SNMP and TCP usage and sampling configuration.

