This article will describe how Domotz can help you troubleshoot various network issues.
Our software comprehensively analyzes network performance, identifies bottlenecks, and investigates connectivity issues across LAN, wireless, and enterprise networks.
Our Network Troubleshooting feature lets you easily recognize and address different LAN issues, such as IP conflicts and DHCP request floods. As well as WAN connectivity issues like Bufferbloat, being able to track important factors like jitter, packet loss, and latency.
The Network Troubleshooting Monitoring Table
To get a comprehensive overview of the overall network status on all your sites, you might enable the “Network Troubleshooting” monitoring table.
To do that, you might create a new Domotz monitoring dashboard and select the “Network Troubleshooting” widget at the top left:
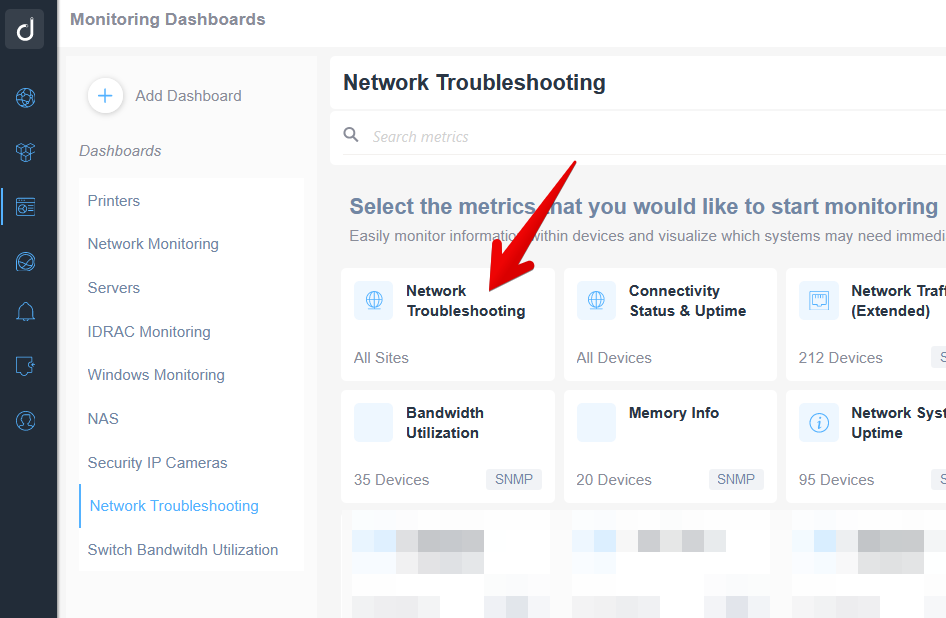
After that, you will be able to define the columns and the list of the sites you would like to monitor, resulting in the following table:
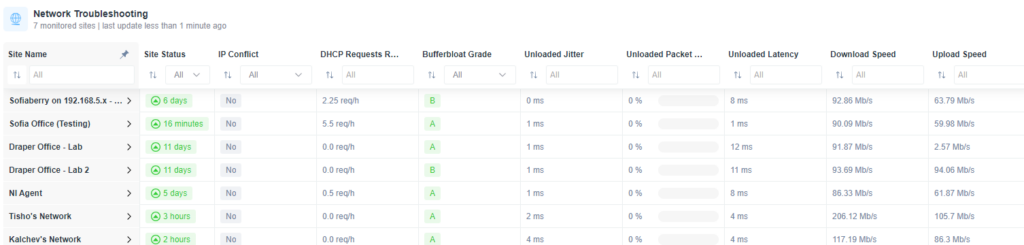
Network Troubleshooting table columns explained
IP Conflict
Domotz can identify any duplication of IP address in your network. This value can be No or Conflict.
DHCP Request Rates
This column displays the hourly rate of the DHCP requests in your network.
Monitoring suggestions:
| Value to be alerted | Alert Condition (if the value is) | Condition value | Notes |
| DHCP Request Rates | Is Greater Than or Equal To | — | see below |
You need to set the value depending on your network type. A guest Wi-Fi network can have many DHCP requests, while a closed office network can have a low number of DHCP requests.
Understanding Elevated DHCP Request Rates
The number of DHCP requests per hour that is considered “high” depends on network size, device types, and normal usage patterns. An excessive volume of DHCP requests may signal network misconfigurations or potential security threats.
Typical DHCP Request Rates
Expected DHCP request rates vary based on network scale:
- Small Networks (1-50 devices): 10-100 requests per hour
- Medium Networks (50-500 devices): 100-1,000 requests per hour
- Large Enterprise Networks (500+ devices): 1,000-10,000+ requests per hour
Identifying Excessive DHCP Traffic
A significantly high rate of DHCP requests may indicate an issue. General thresholds include:
- Small Networks: Over 200-300 requests per hour
- Medium Networks: Exceeding 2,000-5,000 requests per hour
- Large Networks: More than 10,000 requests per hour
If your network experiences an unusually high DHCP request rate, further investigation may be necessary.
Potential Causes of High DHCP Request Rates
- Frequent IP Renewals: Short lease durations (e.g., 5-10 minutes) cause devices to request new IP addresses more frequently.
- Unstable Devices: Devices repeatedly disconnecting and reconnecting can generate excessive requests.
- Network Loops or VLAN Misconfigurations: These issues may result in duplicated or amplified DHCP requests.
- DHCP Starvation Attacks: Malicious users or faulty devices may flood the DHCP server with requests, depleting available IPs.
- Misconfigured DHCP Relay Agents: Improper configurations can cause duplicate requests to be forwarded multiple times.
Troubleshooting High DHCP Request Rates
To diagnose and mitigate excessive DHCP traffic, follow these steps:
By proactively monitoring DHCP request patterns and optimizing network configurations, administrators can prevent performance issues and ensure smooth IP address management.
DHCP Requesters Identification
By clicking on the “View Details” > icon in the DHCP Requests Rates cell, you will be able to see the DHCP Requesters:
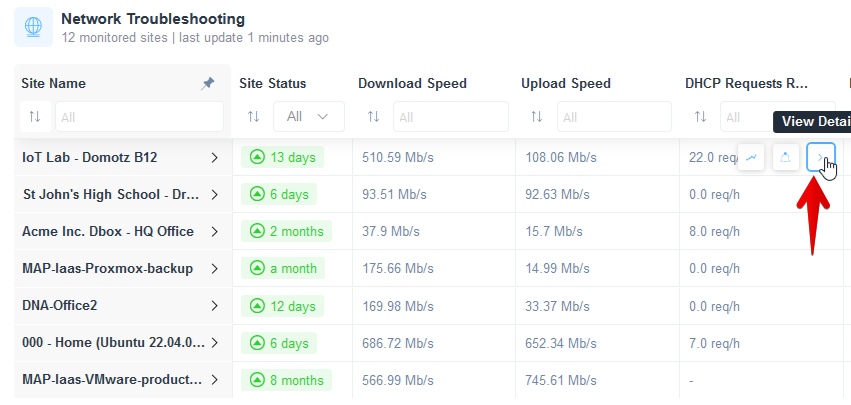
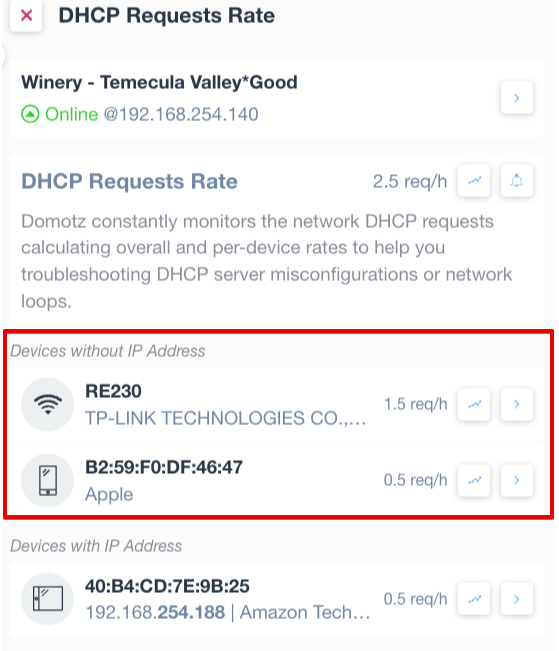
In the right side panel, you’ll see two sections. One called “Devices with IP Addresses”, which will display devices that have a high rate of DHCP requests:
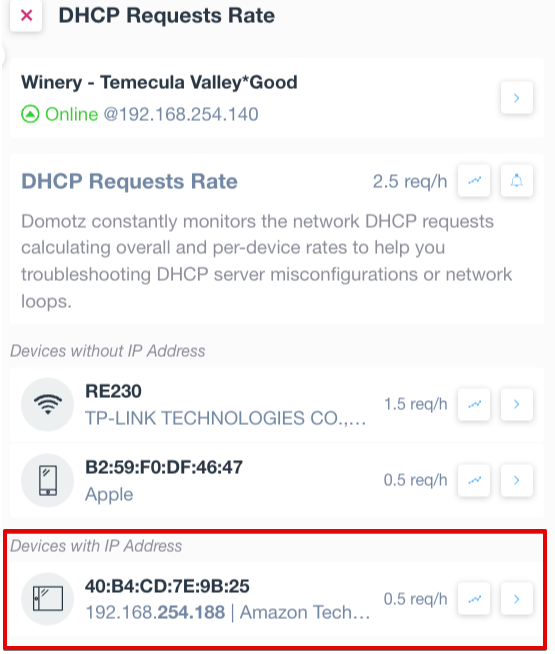
There is another one called “Devices without IP Address”, which shows a list of devices that were not able to get an IP address from the DHCP server:
Bufferbloat Grade
A Bufferbloat is a problem that arises when excessive buffering of data packets causes high latency and poor network performance. This issue can result from various factors, including misconfigured network equipment, large buffer sizes set by default in some devices, or the use of Quality of Service (QoS) mechanisms that prioritize certain types of traffic.
Domotz offers a solution to identify this network phenomenon by providing a grading system for internet connection performance:
- A+ (less than 5ms latency increase)
- A (less than 30ms latency increase)
- B (less than 60ms latency increase)
- C (less than 200ms latency increase)
- D (less than 400ms latency increase)
- F (400ms or more of latency increase)
Monitoring suggestions:
| Value to be alerted | Alert Condition (if the value is) | Condition value | Notes |
| Bufferbloat Grade | Is Greater Than or Equal To | 200 | see below |
When onboarding the network, please see the “grade” displayed on the table to identify any issue with the BB, then set monitoring as explained above.
Below is an example of Grade D:
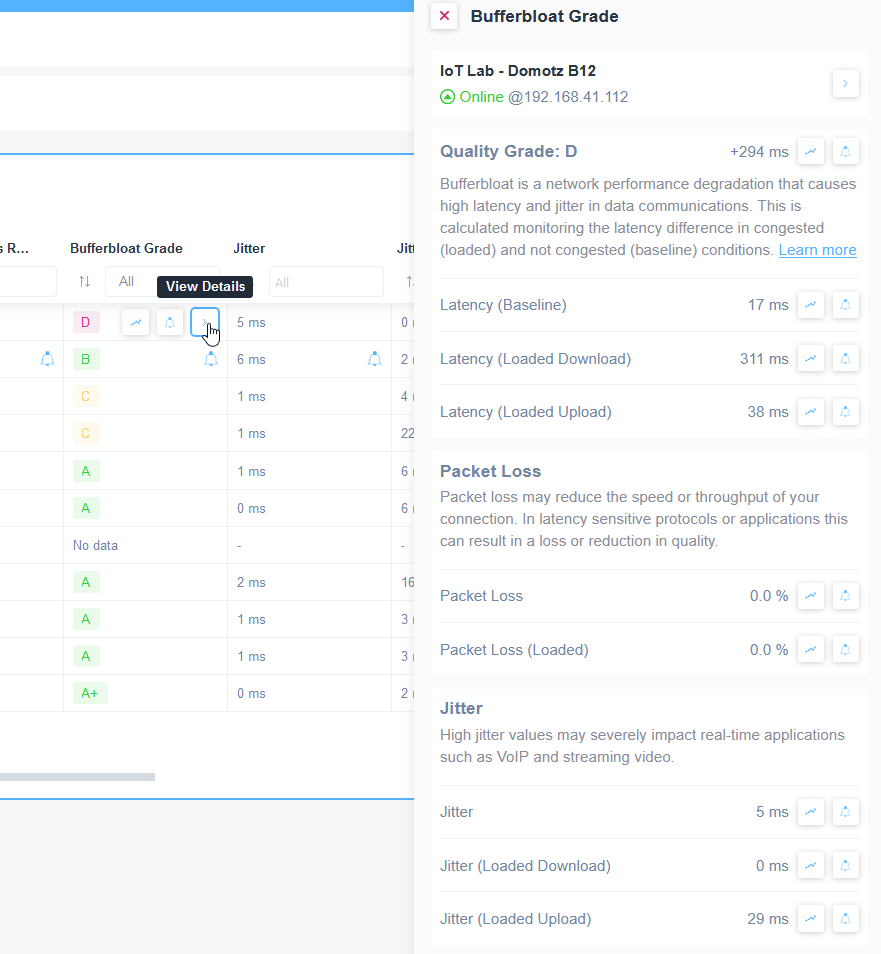
Jitter (unloaded)
Jitter refers to the variation in the delay between packets or data packets reaching their destination. It represents the inconsistency or fluctuations in packet delivery timing. This value is measured in milliseconds (ms) and can significantly impact real-time applications that require consistent and predictable data transmission. Therefore, it is crucial to track this value within a network. The measurement is performed towards Google’s public DNS.
Monitoring suggestions:
| Value to be alerted | Alert Condition (if the value is) | Condition value | Notes |
| Jitter | — | — | see below |
The ‘Alert Condition’ and the ‘Condition value’ for the Jitter should be determined only after Domotz has aggregated various samples. In this way, we can understand, based on the graph of values, what the trend of this indicator is.
Packet Loss (unloaded)
The column displays the packet loss of the Internet connection measured towards Google public DNS.
Monitoring suggestions:
| Value to be alerted | Alert Condition (if the value is) | Condition value | Notes |
| Packet Loss | — | — | see below |
The ‘Alert Condition’ and the ‘Condition value’ for the Packet Loss, should be determined only afterwards, after Domotz has aggregated various samples. In this way, we will be able to understand, based on the graph of values, what the trend of this indicator is.
Latency (unloaded)
Latency refers to the delay between initiating a request or action and receiving the corresponding response or result. It measures the time data travels from source to destination within a network or system. The measurement is performed towards Google’s public DNS.
Monitoring suggestions:
| Value to be alerted | Alert Condition (if the value is) | Condition value | Notes |
| Latency | — | — | see below |
The ‘Alert Condition’ and the ‘Condition value’ for the Latency should be determined only after Domotz has aggregated various samples. In this way, we can understand, based on the graph of values, what the trend of this indicator is.
Download Speed and Upload Speed
You’ll see the download and upload speed of the Internet connection at a specific site in these columns. The Domotz Collector obtains these measurements towards a selected service for the speed test feature. For more information, please refer to this link: https://help.domotz.com/monitoring-management/network-performance/#htoc-speed-test.
Monitoring suggestions:
| Value to be alerted | Alert Condition (if the value is) | Condition value | Notes |
| Download Speed | — | — | see below |
| Upload Speed | — | — | see below |
The “Alert Condition” and the “Condition value” for the download and upload speed should be determined only after Domotz has aggregated various samples. In this way, we can understand, based on the graph of values, what the trend of this indicator is.
Network Troubleshooting Events
IP Conflict event
Once this occurs, the Domotz account Team Leader will immediately receive an email that will open the incident and report the devices involved in the issue:
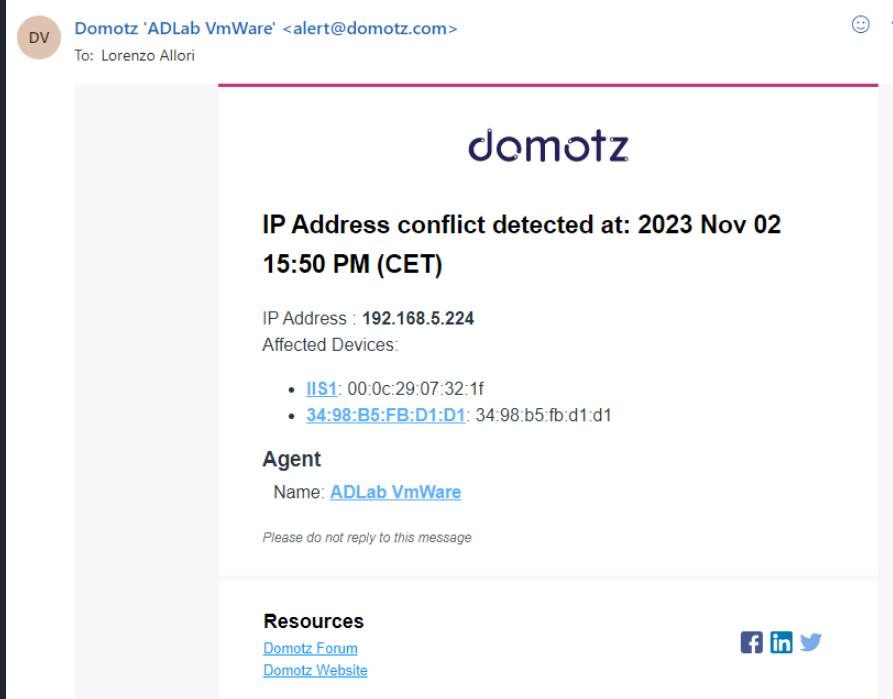
By clicking on the links, you will be able to access them in Domotz.
Also, on each of the devices involved, the IP conflict event will be visible in the “Latest Events” section:
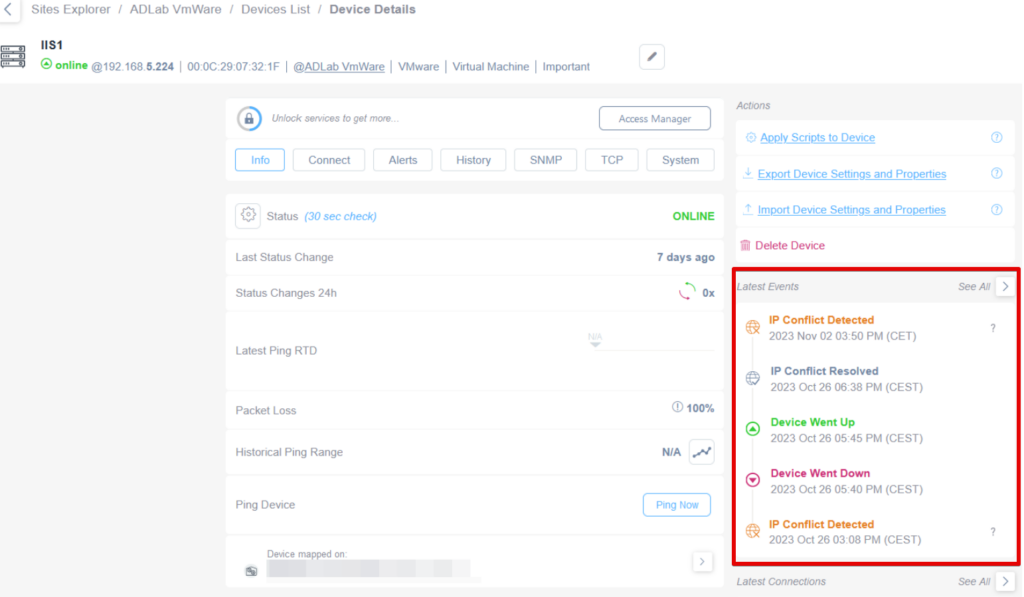
Once you resolve the issue, the Team Leader will receive an “Incident resolved email”:
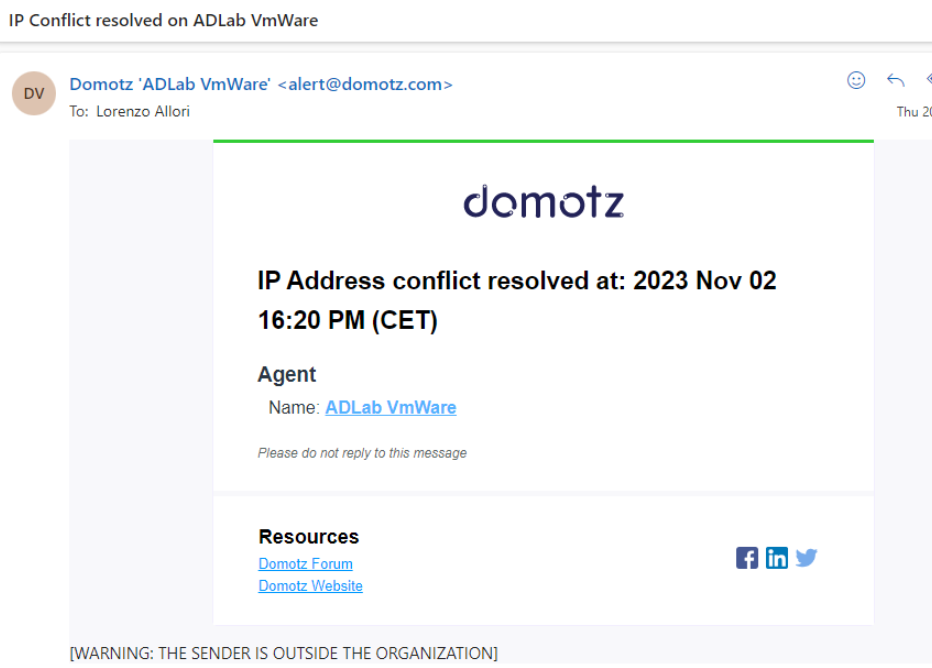
How to resolve an “IP Conflict” event
IP conflicts occur when two devices on a network are assigned the same IP address, resulting in connectivity issues and network disruptions. Resolving an IP conflict requires identifying the cause and implementing appropriate solutions. Here are some possible causes and resolutions for IP conflicts:
1) Manual IP Address Assignment
- Cause: Manually assigning IP addresses to devices without considering the existing IP allocations can lead to conflicts.
- Resolution: Ensure that IP addresses are assigned dynamically through DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to avoid conflicts. Configure your network devices to obtain IP addresses automatically.
2) DHCP Server Misconfiguration
- Cause: A misconfigured DHCP server may unintentionally assign duplicate IP addresses.
- Resolution: Verify the DHCP server settings and ensure the pool of available IP addresses is correctly configured. Restarting the DHCP server or renewing the IP lease for affected devices may resolve conflicts.
3) Duplicate Static IP Assignment
- Cause: Manually assigning the same static IP address to multiple devices.
- Resolution: Check the network settings of all devices involved and ensure each has a unique static IP address. Assigning a different IP address to one of the conflicting devices should resolve the conflict.
4) Network Device Malfunction or Reset
- Cause: Malfunctioning network devices or devices that have been reset to default settings can result in IP conflicts.
- Resolution: Restart the affected devices and check their network settings. Verify that they are configured to obtain IP addresses automatically. If necessary, assign new IP addresses to the devices manually.
5) Rogue DHCP Servers
6) Network Segmentation Issues
- Cause: Improper network segmentation or misconfigured VLANs can lead to IP conflicts.
- Resolution: Review the network segmentation and VLAN configurations. Ensure that devices are properly assigned to their respective VLANs and that IP address ranges do not overlap between segments.
7) Network Monitoring and Troubleshooting Tools
- Cause: Inadequate network monitoring and troubleshooting tools may make identifying and resolving IP conflicts difficult.
- Resolution: Deploy network monitoring and troubleshooting tools, such as Domotz, that provide real-time visibility into IP address allocations, detect conflicts, and assist in resolving them effectively.
Remember, each network environment is unique, and the specific cause of an IP conflict may vary. By understanding the possible causes and implementing the appropriate resolutions outlined above, you can effectively resolve IP conflicts and maintain a stable and functioning network.
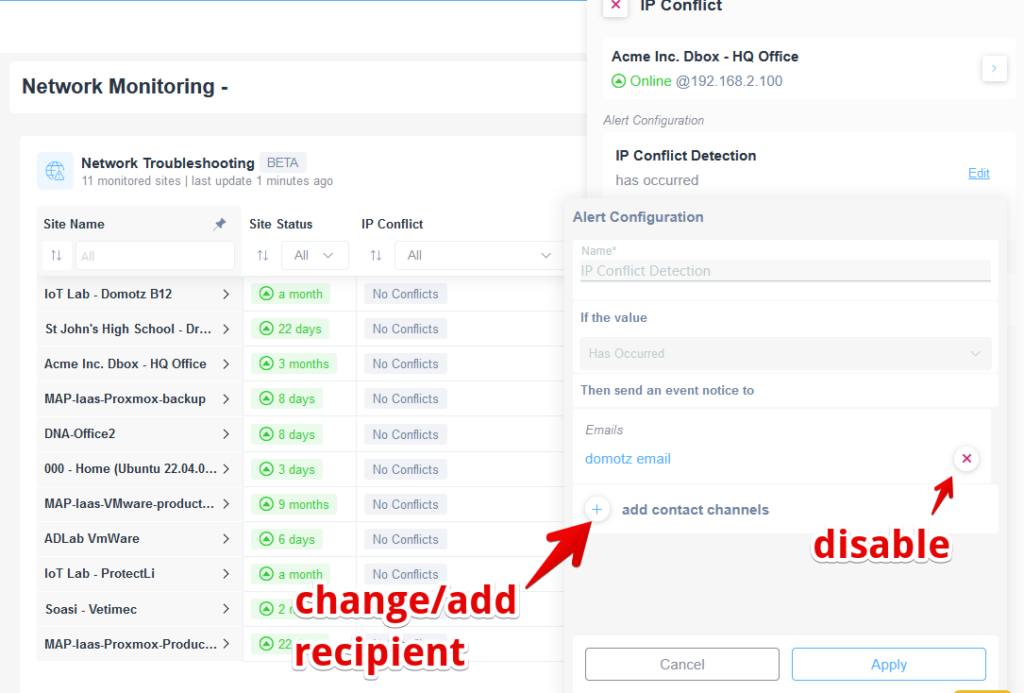
How to disable/change the recipient for the IP Conflict event alert
To disable the IP Conflict event notification or change its recipient, you might access the Network Troubleshooting monitoring table and click on the “View Details” icon, which appears when hovering next to an IP conflict value, and then click “Edit” on the right-side panel:
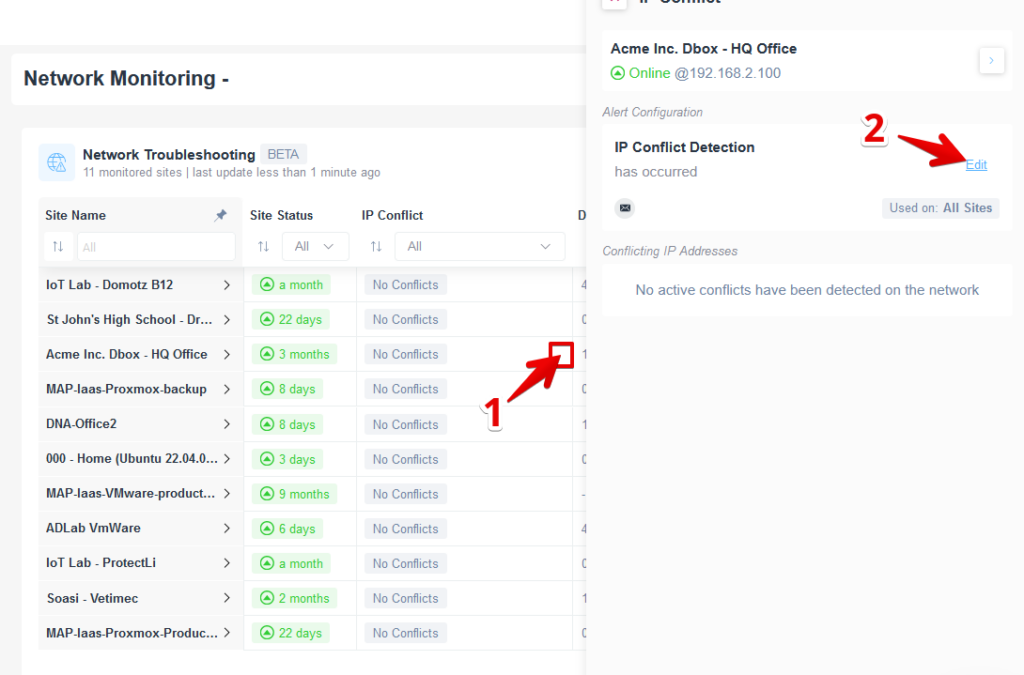
To disable, click the red x, or to edit the change the email recipient for the notification, add a ticketing system or a webhook such as Slack, please select the + button at the left of the “add contact channels” label: