The RBAC feature in Domotz allows you to manage user access and permissions by assigning specific roles to users. You can create multiple users with distinct roles, ensuring that each user has access to only the resources and functions necessary for their job. This enhances security and streamlines the management of users across different teams or clients. Each role can have varying levels of access, such as read-only, admin, or custom roles, providing flexibility in controlling user permissions within the Domotz platform.
- Feature Enablement
- Managing Users, Groups, Roles and Permissions
- Overview
- Getting Started with Access Management (RBAC)
- How to use RBAC Access Management
- Key Concepts
- Default Roles and Corresponding Groups
- Recommended Role Stacking Strategy
- How to Set It Up
- Managing Changes
- Example Scenario: Scaling Admin Access Across Two Regions
- Best Practices
- Summary
Feature Enablement
How to enable Access Management (RBAC) for your account
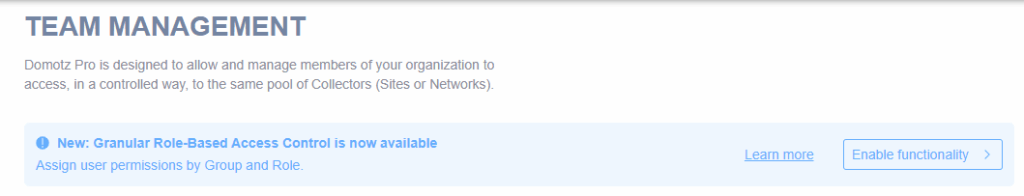
If your account currently uses the Team Management system to manage Users and Roles, and you have an eligible account, the account owner will see a banner with an option to enable RBAC on the Team page in the Domotz portal.
Please ensure that you read the information below about unsupported accounts and the migration process from the current Team Management system to RBAC to ensure that you are ready to enable the feature for your account.
Unsupported Account Types and Functions
The following account types and functions are not supported for Access Management (RBAC). Please reach out to support@domotz.com for more information and assistance.
- Company Structure Accounts: Accounts which utilize the company structure for managing collector access and migration between accounts/teams is not supported by RBAC at this time. If you would like to adopt RBAC to more tightly control User permissions, please contact us and we can discuss such a transition with you.
- Collector Collaboration and Collaborated Collectors: Manual User enablement of RBAC for accounts where collectors have been collaborated to other Users, or accounts with access to collaborated collectors are not supported.
- RBAC is meant to replace the need for collaboration since it provides the means to grant external Users access to your Domotz account and tightly control permissions for such Users.
- If RBAC is enabled for these accounts, Users will lose access to manage collector collaboration and will lose access to any collaborated collectors.
- If you would like to enable RBAC for your account, we can help you transition from using collaboration to adding these Users directly to your account using the new RBAC system, ensuring they have the appropriate permission levels.
Enablement and Migration Process: Team Management to Access Management (RBAC)
When your account owner selects to enable RBAC from the Team Management menu, they will receive a pop-up with an overview of the process described in more detail below. When you confirm this message, RBAC will be enabled for your account. As part of the User and Role migration to RBAC, the following automatic Role and Group assignments will be made to preserve your current access model under Team Management:
- Account Owner: Will be assigned to the Administrators Group and given the Administrator Role, providing full access to all features and settings, including subscription and User management. This Group and the Role permissions cannot be changed, but you can add users to the Administrators Group to extend full access to them as well.
- Team Members: Will be assigned to a Team Members Group and given the Team Member Role, which mirrors the current permissions and so excludes Access Management (RBAC) and Billing functions.
- Field Operators: WILL BE MIGRATED AS USERS ONLY, without any Group or Role assignments. Groups and Roles will need to be created and assigned to these Users in order to restore access to specific collectors and overall permissions appropriately. MAKE SURE TO SAVE THE COLLECTOR ASSIGNMENTS FOR THESE USERS TO ENSURE THEY CAN BE RESTORED CORRECTLY ONCE RBAC IS ENABLED.
Managing Users, Groups, Roles and Permissions
Overview
RBAC Concepts Overview
RBAC introduces three key components:
- Users: Individual people who access the Domotz platform.
- Groups: Logical collections of Users (e.g., Field Technicians, Network Admins) that allow you to centrally apply permissions. Roles are assigned at the Group level and automatically apply to all Users within the Group.
- Roles: Sets of permissions that define what actions Users can perform. Roles are assigned to Groups, and Users inherit permissions through Group membership.
Permissions Configuration
All permissions are configured using a Role and fall into three overall categories:
- Portal/Global level permissions which include settings such as:
- Permissions such as collector addition/deletion/cleanup, setting devices as managed, Organization management, and management of custom filters
- Billing and Branding management
- Account level permissions which include settings such as:
- Alerts settings for managing alert profiles and contact channels
- Integration settings for management of integrations and scripts
- Monitoring dashboards management for view vs. management access to all or selected dashboards
- Device Profile access for view, manage, and application to devices.
- Collector level permissions include:
- Collector access to all or only selected collectors and their devices
- Collector Configurations to manage collector settings, VPN connections, and deletion of devices (restricting collector configuration renders all collector settings as read-only)
- Device Management which when restricted, removes all management capabilities for devices, rendering them as read-only
Getting Started with Access Management (RBAC)
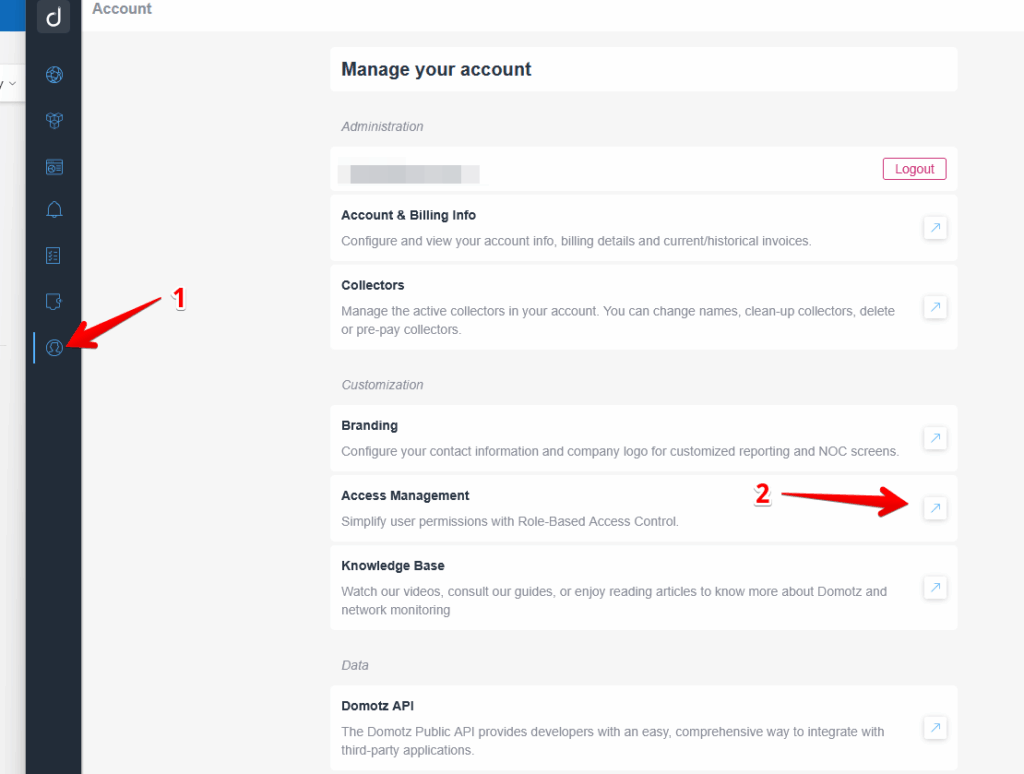
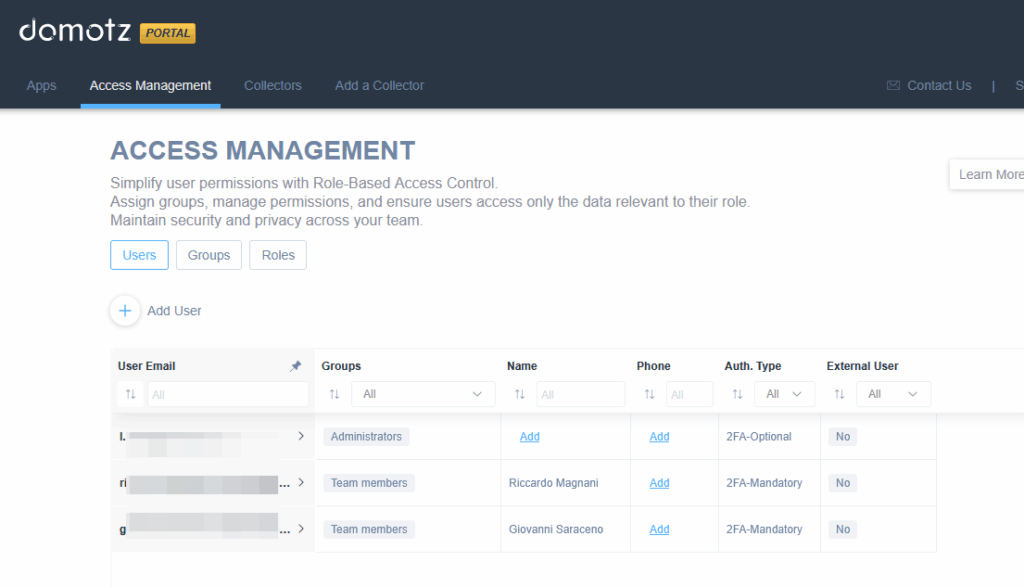
This view in the Domotz Portal allows you to:
- Review existing Users and verify their Group and Role assignments. (As noted in the Enablement and Migration Process above, any prior Field Operator Users will have been migrated as Users only without any permissions so they will need access restored via Group and Role assignments.)
- Review the predefined Roles and respective Groups or create your own.
- Assign Users to Groups to inherit the correct permissions based on the Role(s) assigned to those same Groups.
How to use RBAC Access Management
Domotz Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) allows you to manage Users, Groups, and Roles flexibly and for scalability. You can stack multiple Roles in Groups to separately manage:
- Collector and Dashboard Access (collector and dashboard access and permissions)
- Permission Access (overall account and portal level permissions)
This structure simplifies permission management across multiple collectors and teams.
Key Concepts
Users
- An individual User account in your Domotz environment. Users are assigned to Groups, not directly to Roles.
- Permission Inheritance: A User inherits the permissions based on their Group membership(s) and the permissions allocated to the Roles assigned to those Groups. If a User inherits permissions from multiple Groups/Roles which are for the same permission, then the highest level of access wins. For example, if the Collector Configuration permission is denied by one Role but granted by another, then access for managing Collector Configuration is granted.
- Permissions Overview: User permissions can be viewed by using the Actions > Permissions option which will display all permissions that are granted to a given User.
- External User: This flag can be used to easily track external Users, such as your customers, which have been added to your Domotz account. This will also prevent these Users from receiving any marketing communications from Domotz.
Groups
Groups are collections of Users that inherit one or more Roles. Groups enable mass User management by applying Roles to multiple Users at once.
Roles
Roles define sets of permissions and more than one Role can be assigned to a given Group. When using such an approach (“role stacking”) there are two main types of Roles which we recommend:
- Access Roles: Define where Users can operate and what they can do (specific collectors and their devices, and/or dashboards).
- Permission Roles: Define what actions Users can perform (account-level or portal-level administrative rights such as managing alert settings or integrations and scripts).
Default Roles and Corresponding Groups
Upon RBAC enablement, a set of default Roles and corresponding Groups will have already been created. You can use these Roles as examples for how Roles can be defined and linked to Groups, but also modify them and create your own. (NOTE: The Administrator Role is the only Role which cannot be updated and provides full access to all Domotz features and functions.)
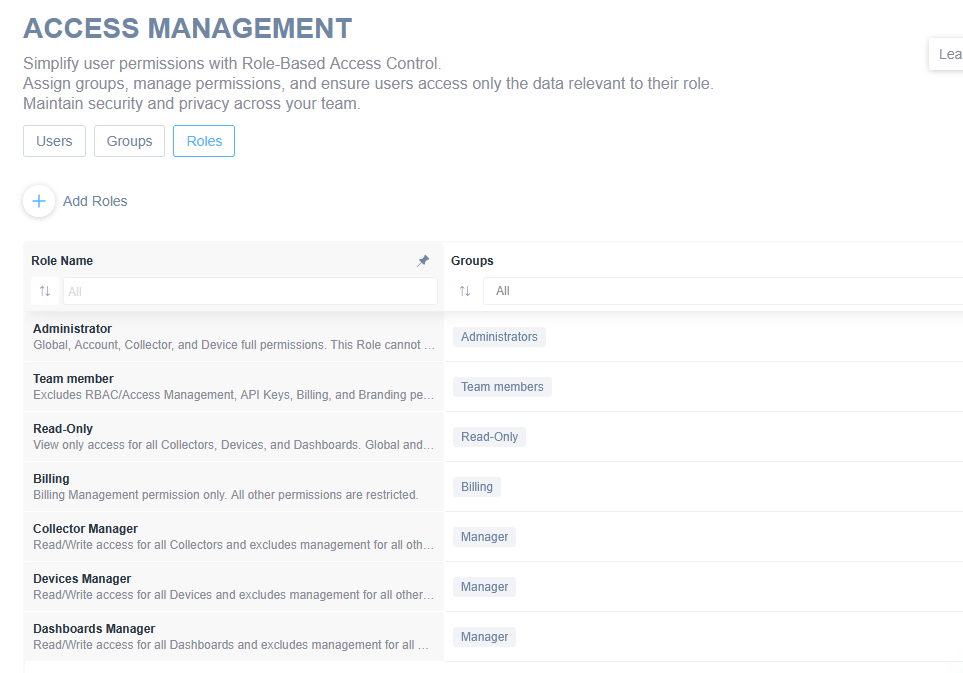
Default Roles
Administrator: Global, Account, Collector, and Device full permissions. This Role cannot be edited or deleted.
Team member: Excludes RBAC/Access Management, API Keys, Billing, and Branding permissions by default. Other Administrator permissions included.
Read-Only: View only access for all Collectors, Devices, and Dashboards. Global and Account level permissions are excluded.
Billing: Billing Management permission only. All other permissions are restricted.
Collector Manager: Read/Write access for all Collectors and excludes management for all other permissions.
Devices Manager: Read/Write access for all Devices and excludes management for all other permissions.
Dashboards Manager: Read/Write access for all Dashboards and excludes management for all other permissions.
Default Groups
Administrators: Administrator Role is assigned to this Group. The linking of this Role and Group cannot be changed, but more Users can be assigned to this Group, and the Administrator Role can be assigned to other Groups if so desired.
Team Members: Team member Role is assigned to this Group by default.
Read-Only: Read-Only Role is assigned to this Group by default.
Billing: Billing Role is assigned to this Group by default.
Manager: Collector Manager, Devices Manager, and Dashboards Manager Roles are all assigned to this Group by default. This provides an example of role stacking.
Recommended Role Stacking Strategy
Instead of creating a unique role for every combination of access and permissions:
- Create a standard Permission Role (e.g.,
Tech-Permissions) - Create different Access Roles for collectors and their devices as well as dashboards (e.g.,
Region-A-Access,Region-B-Access) - Assign both the Permission Role and the appropriate Access Role(s) to the Group
This way:
- Permission changes only require updating the Permission Role.
- Access changes only require updating the Access Role.
- Users automatically inherit updates without manual changes.
How to Set It Up
1. Create Permission Roles
Define a set of permissions needed for typical User activities.
Example:
- Role Name:
Tech-Permissions - Access Scope: Don’t select any collectors. Use this only to define admin and account level permissions.
- Permissions: For example, Add/Cleanup Collectors, Manage/Unmanage Devices, Alert Settings
Steps:
- Click Add Role
- Select the appropriate Portal and Account-level permissions.
- Save the Role.
2. Create Access Roles
Define access based on collectors or environments Users need.
Example:
- Role Name:
Region-A-Access - Access Scope: Only Region A collectors and dashboards
- Permissions: Collector and dashboard specific permissions
Steps:
- Click Add Role.
- Select only the appropriate collectors and dashboards and their respective permissions
- Save the Role.
3. Create Groups
Group Users by function or team while stacking multiple Roles.
Example:
- Group Name:
Region A Techs - Assigned Roles:
Tech-PermissionsRegion-A-Access
Steps:
- Click Add Group.
- Assign Users to the Group.
- Assign both the Permission Role and the Access Role.
- Save the Group.
4. Assign Users to Groups
Users inherit all Roles and their permissions assigned to their Group(s).
Steps:
- Add or Edit a User.
- Assign the User to the correct Group(s).
Managing Changes
Updating Permissions Globally
If you modify a Permission Role, all Groups (and therefore all Users) with that Role automatically receive the updated permissions.
Example: If Tech-Permissions gains a new “Delete Collectors” permission, every Group using that Role will immediately inherit it.
Adding or Removing Collector Access
If a User needs access to a new collector:
- Modify an existing Access Role to grant access to the new collector.
- Add an existing or create a new corresponding Access Role with that collector access and add it to their Group.
Example Scenario: Scaling Admin Access Across Two Regions
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|
| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create Tech-Permissions Role | Defines tech-level permissions. |
| 2 | Create Region-A-Access and Region-B-Access Roles | Restrict permissions for collectors and dashboards to each region. |
| 3 | Create Region A Techs Group | Assign the Tech-Permissions + Region-A-Access Roles. |
| 4 | Create Region B Techs Group | Assigns the Tech-Permissions + Region-B-Access Roles. |
| 5 | Assign Users | Users inherit permissions and region access automatically. |
| 6 | Change Permissions | Edit Tech-Permissions once to update both Groups instantly. |
Best Practices
- Standardize Permission Roles: Fewer permission Roles = easier management.
- Separate Collector and Dashboard Access from Global and Account level Permissions: Cleaner group structures and easier scaling.
- Use Clear Naming Conventions: Example:
Region-A-Access,Tech-Permissions. - Audit Roles Periodically: Check for redundant or unused Roles.
Summary
By using Role Stacking in Domotz RBAC:
- You simplify User, Group, and permission management.
- You ensure consistent, scalable permission enforcement.
- You reduce manual effort when access or permissions need changes.

