Prerequisites
Before proceeding please check that the machine hosting the Domotz Collector is plugged in on to a trunk port of your switch which is able to see all your VLANs.
Configuration
With recent changes on how Windows manage network, with components from Hyper-V that is now installed by default, it is now possible to configure VLANs without third-party software.
It is a 3-step process, create a virtual switch, create a virtual network interface and set this vNIC in access mode to the VLAN you want to monitor.
1. Create Virtual Switch
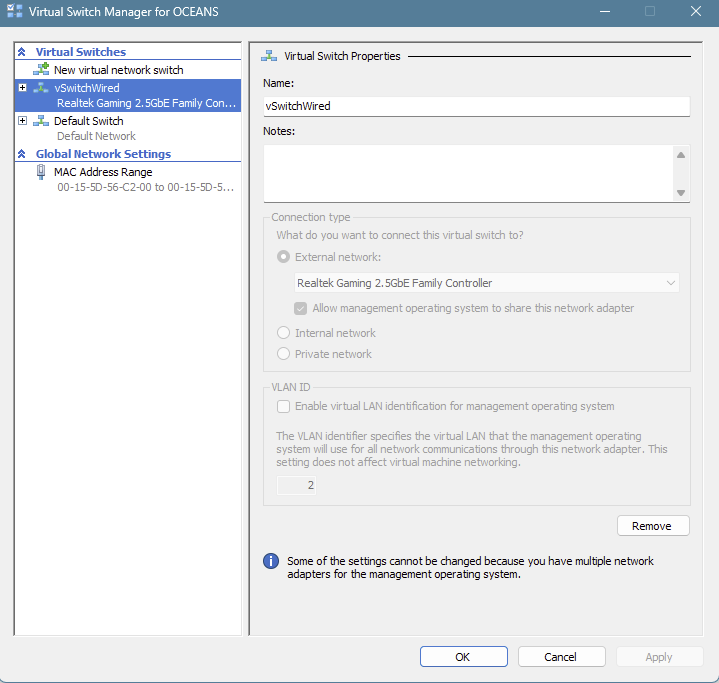
If you have Hyper-V installed you can use GUI to create a Virtual Switch connected to the host physical NIC attached to a switch port that is allowed into the VLANs you want to monitor.
Open the Hyper-V Manager and select the Virtual Switch Manager:
You can also create the Virtual Switch manually using PowerShell in administrator mode if you don’t have the Hyper-V Manager installed:
a) List the NICs you have attached to the host:
Get-NetAdapter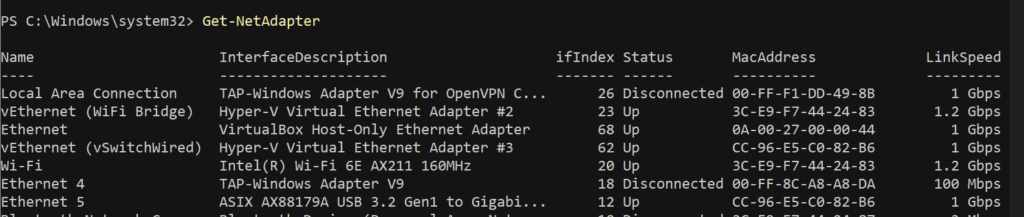
b) Create the Virtual Switch attached to the interface:
New-VMSwitch -Name "vSwitchWired" -NetAdapterName "Ethernet 5" -AllowManagementOS: $true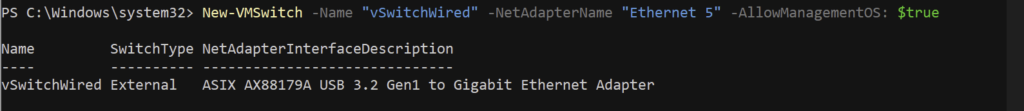
2. Create Virtual NIC (vNIC)
Add-VMNetworkAdapter -ManagementOS -Name "VLAN66" -SwitchName vSwitchWired3. Set the vNIC to access mode on the VLAN you want to monitor
Set-VMNetworkAdapterVlan -ManagementOS -VMNetworkAdapterName VLAN66 -Access -VlanId 666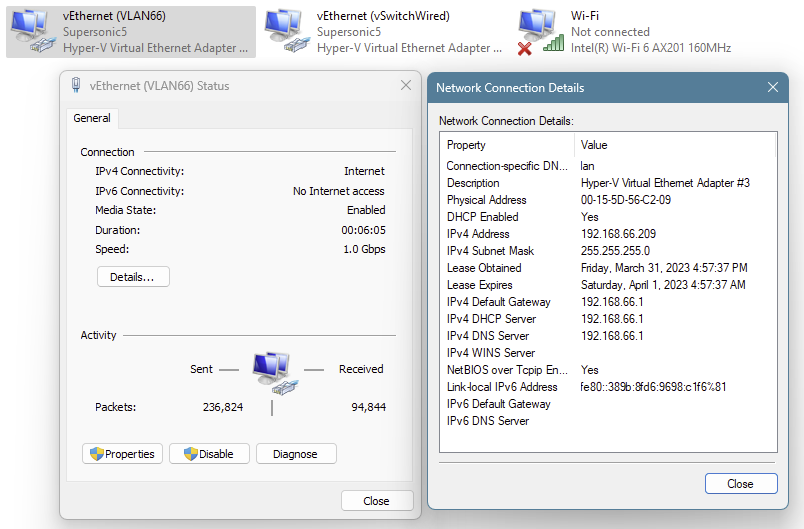
Repeat the steps 2 and 3 for all VLANs you want to monitor.
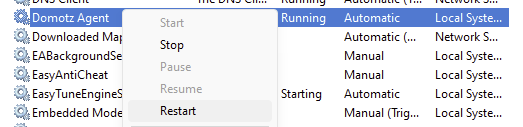
Since these vNICs are newly created, please restart the Domotz Agent service to accelerate their detection. This will restart the Collector and trigger an immediate NIC scan.
You can do this from the Services (services.msc) applet. Locate Domotz Agent, right-click it, and select Restart”:
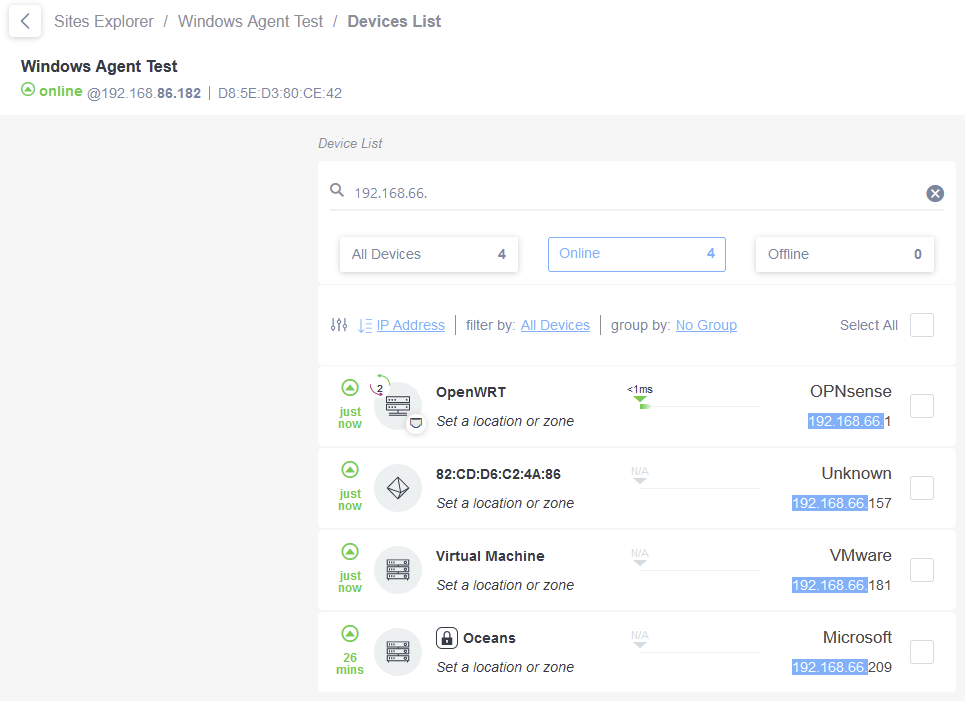
Within some minutes , the Collector will report devices from the additional VLANs as online:
Note that depending on the NIC you have installed on your host, you may be able to manage these virtual interfaces connected to VLANs using their proprietary tool, see below two examples.
Realtek NICs
If you are using a Realtek NIC, you have to install the Realtek Ethernet Diagnostic Utility and with that Tool configure the additional VLANs:

A new Virtual Interface will be created for each VLAN you add for both Intel or Realtek.
Intel NICs
If you use Intel NICs, here they have more details about the models and how to do it: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/support/articles/000005677/network-and-i-o/ethernet-products.html\
Other NICs manifacturers
Other brands may have a similar tools, you might check their website.



